SAP Goes Beyond Net Zero With Contributions to Global Climate Projects
Feature by Alexa MacDonald
Starting in 2024, SAP is doubling down on its net-zero strategy by expanding its commitment to nature conservation and making financial contributions to climate projects.
The financial contribution will support carbon removal and carbon reduction projects:
- Carbon removal projects: These projects remove carbon emissions from the atmosphere and store them for decades – in an ideal scenario, the storage is permanent. Examples include nature-based and technical solutions such as reforestation, where trees store carbon emissions in their biomass as well as direct air capture and storage technologies.
- Carbon reduction projects: Also known as carbon avoidance projects, these projects prevent additional carbon emissions from entering the atmosphere, reducing the overall amount of carbon emitted. Examples include avoided deforestation or energy efficiency projects.
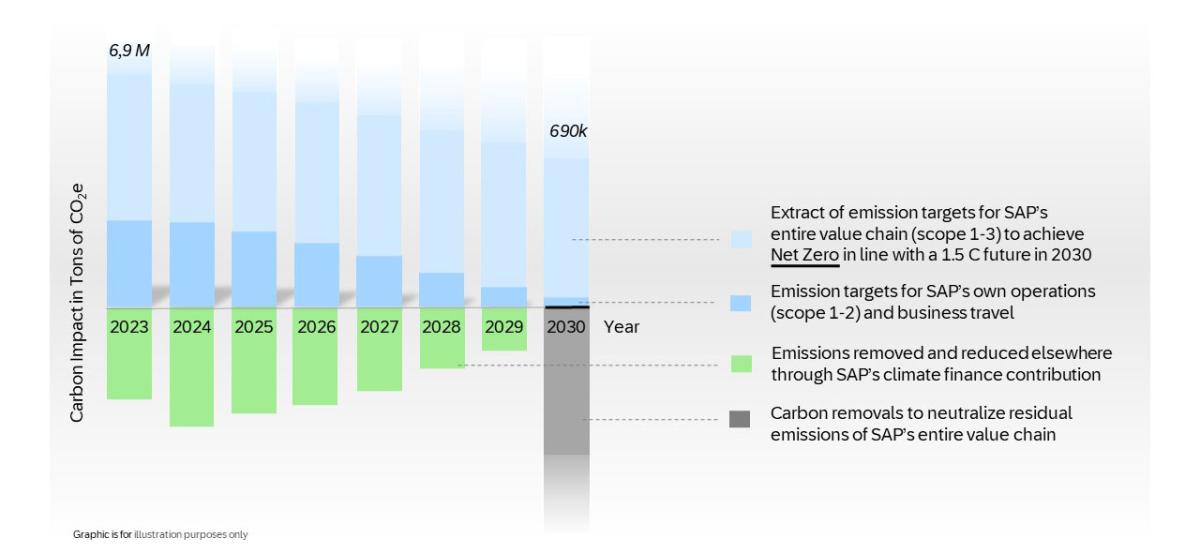
This doubling down on its net-zero strategy follows SAP’s successful delivery on its pledge to become carbon neutral in its own operations in 2023 by balancing out unavoidable emissions with carefully selected carbon credits. While the company’s use of the statement “carbon-neutrality” will be discontinued, the dedication to reduce its carbon footprint and finance climate action beyond its own value chain remains strong.
Net zero is a state where the greenhouse gases going into the atmosphere are balanced by removal out of the atmosphere. There are a number of definitions of net zero and how companies can achieve it. SAP follows the Science Based Targets initiative’s (SBTi) Net-Zero Standard. Achieving net-zero emissions across our entire value chain means that all our emissions across all emission sources need to be either eliminated or, up to certain limits, compensated for. These emission areas, known as scopes, include those from our own operations, those generated by the energy we purchase to run operations, and finally, the largest area, external emissions such as those incurred by employee travel, items procured, and customer data center use.
SAP Is On Track to Plant 21 Million Trees and Plans More
SAP is on track to meet its 2025 goal of planting 21 million trees and has now raised its reforestation commitment.
By 2030, SAP will support trusted partners and communities to plant and protect a total of 25 million trees helping to conserve diverse forests. Furthermore, SAP will fund the conservation and rewetting of coastal and inland wetlands such as bogs and mangrove swamps. With these conservation initiatives and the increased reforestation pledge, SAP’s goal is to conserve more land than its offices and owned data centers occupy worldwide.
To ensure that selected projects deliver a positive outcome, SAP will continue to apply the rigorous and robust due diligence that has previously informed the selection of successful climate investments such as SAP’s long partnership with Livelihood Carbon Funds (LCF), where SAP has funded the planting of trees in Senegal, Rwanda, India, Indonesia, Guatemala, and Mexico.
Bridging the Gap
SAP firmly believes that financing climate projects beyond a company’s value chain should be an item on every corporate sustainability agenda. As long as it does not undermine current corporate decarbonization programs, the financial muscle of corporations can bridge the gap in parts of the world where fiscal finances are not robust enough to restore ecosystems and build resilient low carbon economies and livelihoods.
This financial contribution will provide quantifiable benefits to mitigate the effects of climate change beyond SAP’s own value chain with investments in projects that deliver a positive impact for the climate, for local and global populations, and for biodiversity.
The level of the financial contribution is determined by SAP’s own emissions in a given year and is disclosed in terms of carbon emissions, since costs for carbon projects can be subject to change.
With this financial contribution and increased commitment to land conservation and reforestation, SAP continues its journey to introduce meaningful measures to achieve net-zero in 2030, 20 years earlier than originally planned.
Financing climate projects at the same time as pursuing its corporate net-zero agenda allows SAP to take responsibility for emissions that cannot be avoided and actively mitigate climate change on a global level. Furthermore, the financial contribution will enable positive climate action on a far greater scale than SAP could achieve alone.
Shifting Perceptions
In the last 15 years, corporate sustainability at SAP has shifted perceptions on how corporations manage their own carbon emissions and how corporate sustainability agendas must be as actionable as they are accountable.
Since 2012, the SAP Integrated Report has shared information on SAP’s annual environmental performance and progress on corporate sustainability targets. SAP has led the way in showing that corporate sustainability is an integral part of business – not just an add-on to strategy or operations.
SAP’s carbon impact is one of the sustainability KPIs that are indicators of future performance and form the basis of compensation elements for members of the Executive Board of SAP SE. Today, sustainability is deeply embedded in SAP’s vision to bring out the best in every business. With its extensive portfolio of sustainability solutions, sustainability is anchored in SAP’s purpose to make the world run better and improve people’s lives.
Connect with SAP News on LinkedIn to stay up-to-date